Telehealth, leveraging technology to deliver healthcare services remotely, has significantly altered the landscape of medical care, making wellness more accessible than ever before. This article delves into the multifaceted role of telehealth in enhancing healthcare accessibility, its benefits, challenges, and the future outlook.
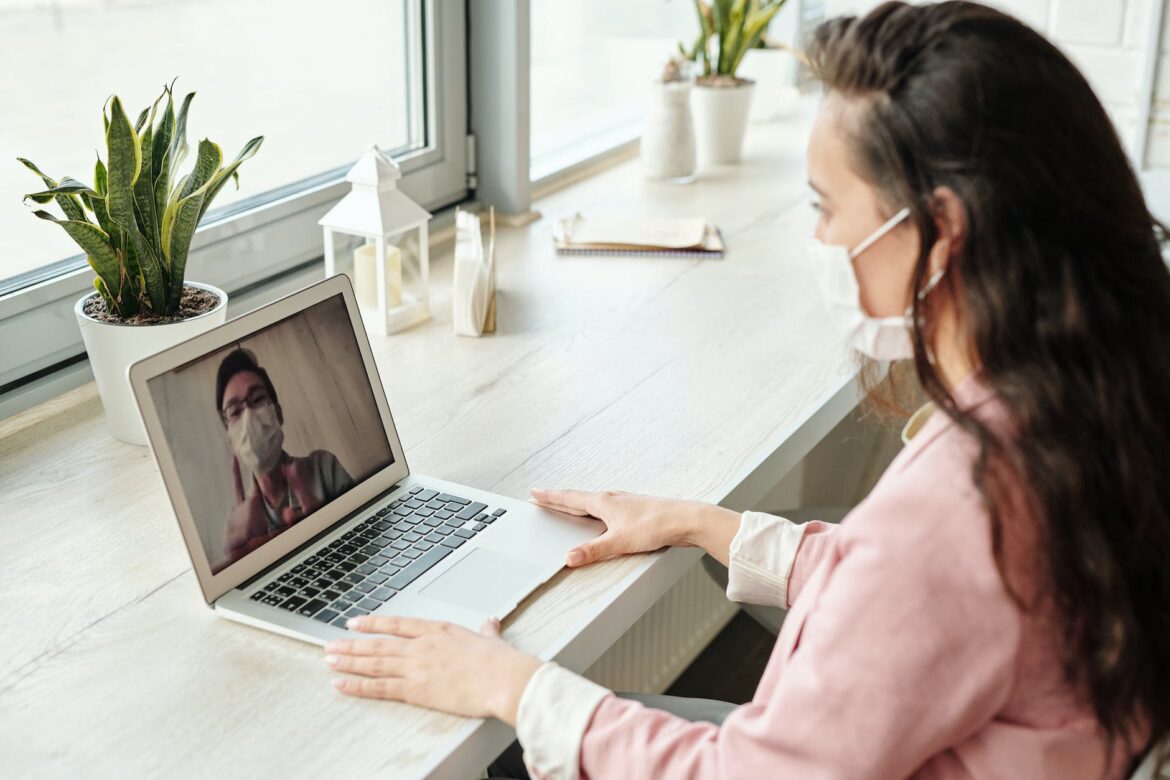
Telehealth has been instrumental in breaking down geographical barriers, providing care to remote, underserved, and disabled populations. By utilizing video calls, messaging, and digital monitoring, telehealth enables patients to access medical consultations, mental health support, and chronic disease management from their homes.
Federal programs like the Affordable Connectivity Program (ACP) and Lifeline have been pivotal in supporting telehealth by assisting eligible households with internet costs, thus ensuring patients can access telehealth services. These initiatives highlight a concerted effort to bridge the digital divide and make telehealth accessible to all.
Telehealth has significantly impacted mental health care and chronic disease management. By offering a discreet platform for therapy and counseling, telehealth addresses the stigma associated with seeking mental health support. For chronic conditions, telehealth empowers patients through remote monitoring and virtual check-ins, enabling proactive management of their health.
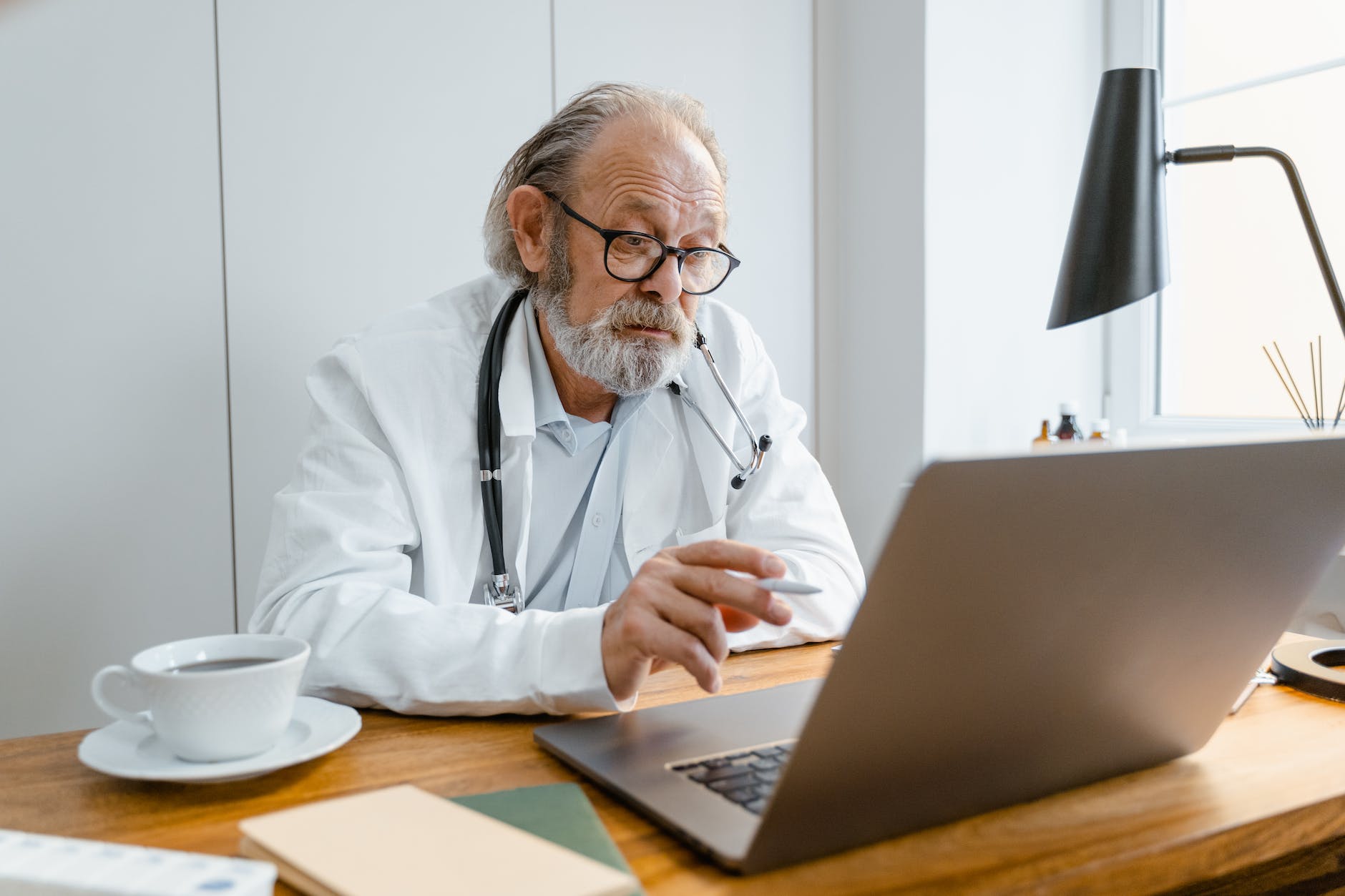

Telehealth leverages various technologies, including patient portals, personal health apps, and electronic personal health records (PHR), to enhance patient engagement and healthcare management. These tools facilitate secure communication between patients and providers, organize medical information, and support self-monitoring of health metrics.
The concept of Digital Determinants of Health (DDoHs) underscores the role of digital literacy, broadband infrastructure, and technology adoption in healthcare equity. DDoHs influence the efficacy of telehealth services, highlighting the need for inclusive design and policies that ensure all population segments can benefit from telehealth.
Despite its benefits, telehealth faces challenges, including potential disparities in access for patients lacking digital literacy or necessary technology. Additionally, the effectiveness of telehealth can be constrained by the limitations of remote assessments and diagnostics, underscoring the importance of integrating telehealth with traditional healthcare services responsibly.
Looking ahead, the integration of telehealth into the healthcare ecosystem presents an opportunity to further democratize access to medical services. Continued advancements in technology, alongside policies aimed at reducing the digital divide, promise to enhance the reach and effectiveness of telehealth services. The ongoing development of policies that support telehealth reimbursement and the adoption of technologies that address the limitations of remote care are crucial for the sustainable growth of telehealth.
In conclusion, telehealth represents a paradigm shift in healthcare delivery, offering a pathway to more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered care. As we navigate the complexities of integrating digital health solutions, the focus must remain on ensuring equitable access and leveraging technology to meet the diverse needs of the global population.